Inter-Company vs Intra-Company STO: What’s the Difference in SAP?

Internal stock flow is equally important in SAP Materials Management as the outward purchase. Companies with multiple plants and codes use Stock Transfer Orders (STOs) to move materials effectively, openly, and under system control. However, one of the most common areas of confusion for learners and professionals is the distinction between Inter-Company and Intra-Company STO.
The post organizes the subject matter in a straightforward, practical, and consistent manner with actual SAP MM scenarios and the learning requirements at SCM-Cloudbook.
What Is STO in SAP MM?
When studying SAP MM, one of the first concepts you will encounter is the term STO and its rationale. STOs are intended to facilitate internal procurement, in which materials are moved between plants rather than purchased from an external vendor.
Definition of STO in SAP
A Stock Transfer Order is a purchasing document used to move materials between plants or company codes within the same organisation. STO in SAP enables the control of stock movements and maintains visibility, planning, and audit trails within the system.
Where STO Fits in the SAP MM Process
STO lies between the inventory management and procurement in the SAP MM lifecycle. It enables material requirements planning (MRP), stock visibility, and logistics execution coordination, without treating the transfer as an external purchase.
What Is the STO Process in SAP?
It is necessary to have a general understanding of the end-to-end mechanism of the STO process before comparing intercompany and intracompany situations. This process ensures traceability of stock movement, planning of stock movement, and proper posting.
Overview of the STO Process in SAP
The SAP process typically begins with the generation of a Stock Transfer Order by the receiving plant. The material will then be shipped by the supplying plant, and a goods receipt will be posted at the receiving plant. This can take the form of deliveries, transit stock, and financial postings, depending on the configuration.
SAP MM STO Process Flow (High Level)
At a high level, the sap mm sto process follows these steps:
- STO creation by the receiving plant
- Outbound delivery from the supplying plant
- Goods issued from the supplying plant
- Goods receipt at the receiving plant
This flow ensures stock accuracy and accountability across locations.
What Are the Different Types of STO Processes in SAP?
The SAP facilitates various STO situations to align with business organisations and legal standards. Learning about these types assists you in selecting the appropriate process for your organisation.
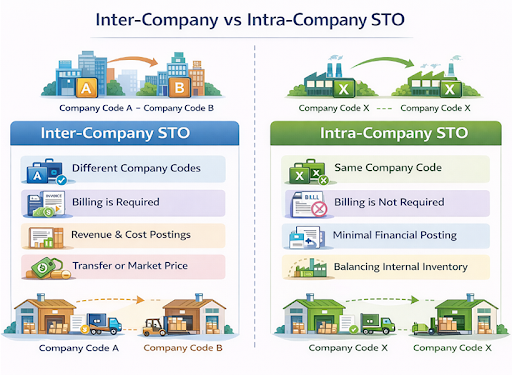
Intra-Company STO
An STO within an intra-company is applied in cases where the two plants are under the same company code. In this case, the company’s moves are without billing or revenue recognition between companies.
Inter-Company STO
Intercompany STO is applied when a supplying and a receiving plant are in two company codes. This usually entails the billing, price terms and financial creditings in between company codes.
What Is the Difference Between Inter-Company and Intra-Company STO in SAP?
This is the most significant and most sought-after comparison for learners of SAP MM. It is not only technical; financial compliance and reporting are also affected.
Key Differences: Inter-Company vs Intra-Company STO
Inter and intra-company STOs differ primarily in company codes, financial implications, and billing. These differences can be used to understand which options of transferring the stock are right in different businesses and business requirements, depending on the business structure and considerations of compliance for SAP MM users.
| Aspect | Intra-Company STO | Inter-Company STO |
| Company Code | Same | Different |
| Billing | Not required | Required |
| Financial Posting | Minimal | Revenue & cost postings |
| Pricing | Not relevant | Transfer or market price |
| Legal Impact | Internal | Legal intercompany transaction |
| Complexity | Low | Higher |
This comparison alone clarifies when and why each STO type should be used.
What Is Inter-Company STO in SAP?
Inter-company STOs are applied in the case of inter-company transfers of stock across code boundaries. Such situations require closer integration among SAP MM, SD, and FI.
Inter-Company STO Process Flow
In an inter-company STO:
- The receiving plant creates the STO
- The supplying plant issues goods via delivery
- Billing is created between company codes
- Goods receipt is posted at the receiving plant
This ensures financial transparency and compliance.
When to Use Inter-Company STO
Inter-company STOs are ideal when:
- Plants operate as separate legal entities
- Financial reporting must reflect revenue and costs
- Transfer pricing or tax rules apply
What Is the Intra-Company STO Process in SAP MM?
The intra-company STO process applies to materials moved among plants within the same company code. The emphasis of this process is on internal inventory movement without a sale or an intercompany invoice.
The receiving plant in SAP MM creates the STO, the supplying plant issues the goods and the receiving plant posts the goods receipt. There is minimal financial impact, as the transaction is conducted within a single legal entity.

Intra STO Process in SAP MM
Intra sto process in sap mm is the relocation of stock within a plant to plant or within the same code of the company. There is no customer or vendor billing, and its only concern is inventory movement.
Business Scenarios for Intra-Company STO
Typical use cases include:
- Balancing stock between regional warehouses
- Supplying production plants from central storage
- Reducing excess inventory at one location
What Is the Two-Step STO Process in SAP?
The STO process in SAP is a two-step process designed to enhance accountability and visibility in stock transfers, divided into two controlled steps. It is popular for tracking in-transit stock, which is of interest.
To start with, the supplying plant issues a goods issue, and the stock is transferred to transit. Once the material is received by the plant, the goods receipt is recorded to finalise the transfer.
Steps in the Two-Step STO Process
The two-step STO process includes:
- Goods issued from the supplying plant
- Goods receipt at the receiving plant
During this time, stock appears as in transit, improving tracking.H3: Why Two-Step STO Is Used
This approach is preferred because it:
- Improves logistics visibility
- Separates dispatch and receipt responsibilities
- Supports transit stock monitoring
Different Types of STO in SAP
The different types of STOs offered by SAP enable SAP to be flexible in handling numerous business situations. This can be achieved by understanding the various forms of STOs so you can choose the best process based on your business’s structure and the required operations.
One-Step STO
The One-Step STO is used for the internal transfer of material between plants within the same company code. The supply of goods in this case is issued directly from the supplying plant and received directly at the receiving plant. This is the most convenient type when stock movements are faster and easier, and the implications for financial transactions are not significant.
Two-Step STO
Under the Two-Step STO process, the stock is issued at the point of supply and then placed in transit. The goods receipt only occurs after the goods arrive at the receiving plant. The method is most favored when the in-transit stock requires real-time tracking and visibility.
Consignment STO
A Consignment STO allows the stock to be shipped to another plant, but until it is consumed or sold by the receiving plant, it remains the property of the supplying plant. The process is commonly used in vendor consignment programs, in which goods are provided but payment is not made until they are consumed.
STO Process Flow and Steps from EWM and TM
The efficiency of the STO process is increased by implementing the Extended Warehouse Management (EWM) and Transportation Management (TM) modules in SAP. The following are the ways the EWM and TM steps can enhance the visibility, logistics execution, and the overall process flow.
Steps in the STO Process with EWM and TM Integration
- STO Creation in SAP MM: The STO is produced by the receiving plant. Integration with EWM ensures that the necessary stock is on hand, and optimization is applied to warehouse processes.
- Outbound Delivery in EWM: After establishing the STO, EWM monitors the outbound delivery process. This encompasses warehouse operations like picking, packing, and staging products.
- Transportation Planning in TM: Prior to the issuance of the goods, SAP TM also plans and optimizes transportation routes, ensuring the goods are delivered in the most effective way possible.
- Goods Issue from Supplying Plant: The SAP MM combined with EWM enables the issuing plant to issue goods without updating stock levels in real time.
- Goods Receipt at Receiving Plant: Upon receiving goods, the receiving plant posts a goods receipt, and the stock is updated in both SAP MM and EWM. Where there is a Two-Step STO, transit stock in TM is followed by the goods until the goods receipt is posted.
- Financial Posting: Based on the type of STO (i.e., intra- or inter-company), SAP provides the correct financial postings, such as invoicing and revenue recognition, for inter-company business.
Benefits of EWM and TM Integration in STO
- Increased Visibility: EWM and TM offer improved real-time tracking of stock items, enabling businesses to monitor them from the supplying plant through to the receiving plant.
- Improved Logistics: TM improves transportation, reducing delivery time and costs, and EWM simplifies warehouse management, improving inventory accuracy.
- Better Control: EWM helps monitor stock levels accurately, and TM enables effective transportation planning to enhance the overall STO process.
STO Important Movement Types
SAP Material Management (MM) determines the types of movements required to regulate stock flow across various locations. These forms of movement are necessary to monitor inventory and ensure that stock movement is in accordance with business and legal regulations.
Movement Types for Intra-Company and Inter-Company STO
- Movement Type 301: It is applied when transferring goods between the supplying and receiving plants within the same company code in an Intra-Company STO.
- Movement Type 351:This is the type of movement applied in Two-Step STO, where it is issued out of the supplying plant to the goods that are under transit until they are received at the receiving plant.
- Movement Type 601: This is normally applied in normal goods receipt of inter-company STO transactions, whereby goods are issued between two company codes.
- Movement Type 641: This type of movement is applied when the goods are received by a consignment STO, the stock belongs to the plant that receives the consignment until it is consumed by the receiving plant.
What Is the Difference Between STO and Purchase Order (PO) in SAP?
Many novices conflate STOs and standard purchase orders. Although they both utilise purchasing documents, the reasons differ substantially.
STO vs PO: Key Functional Differences
Internal procurement is done using an STO, and external vendors are procured using a PO. STOs transport stock within the organisation, whereas POs transport stock from outside the organisation into the system.
What Is the Delivery Type Used for Inter-Company STO in SAP?
Intercompany STOs have delivery types that govern the shipment, issuance, and financing of materials between company codes. They ensure effective integration between logistics and accounting.
Common Delivery Types for Inter-Company STO
SAP manages STO logistics by utilising specific delivery types. These types of deliveries manage the processes of picking, packing, and issuing goods, enabling the seamless movement of stock between different company codes.
What Is the T-Code for Creating STO in SAP?
SAP has specific transaction codes for creating and managing Stock Transfer Orders. These T-codes enable users to perform the STO process step by step in SAP MM.
The T-Code primarily used to create an STO is ME21N, which allows the relevant STO document type to be selected. The creation of T-Codes is further extended to delivery creation, goods issue, and goods receipt to complete the process.
Key T-Codes Used in STO Process
Some commonly used STO-related T-codes include:
- STO creation
- Outbound delivery processing
- Goods issue and goods receipt
These transactions support the complete STO lifecycle.
What Is the Difference Between Inter-Company and Intra-Company Transactions in SAP?
In addition to STOs, the interpretation of intercompany and intracompany transactions can inform the broader SAP process design.
Transactional Differences at a Business Level
Intercompany transactions affect legal entities, financial statements, and tax reporting. On the other hand, intra-company transactions concern operational efficiency and are not influenced by other financial factors.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right STO Type in SAP
It is important to understand the distinction between Inter-Company and Intra-Company STO for a person working with SAP MM. An appropriate decision is made regarding the company’s structure, legal requirements, and financial transparency.
For learners and professionals, acquiring STO concepts provides a solid foundation in SAP logistics and procurement.
If you not only want to learn the theory of STOs but also want to learn how to use SAP MM through practice, on-the-job learning, and career-oriented instruction, SCM-Cloudbook offers well-organised learning programs for both students and professionals.
Contact SCM-Cloudbook today to choose the SAP certification that matches your career vision.
Connect with us directly: Registration Link
WhatsApp: (wa.link/04d8tw or ✆ +91-9289246569).
SCM-CLOUDBOOK
FAQ’s
What is STO in SAP MM?
In SAP MM, a Stock Transfer Order (STO) is a purchasing document used to move materials between plants or company codes within the organisation.
What is the difference between Inter-Company and Intra-Company STO in SAP?
Inter-company STO exchanges stock between company codes with billing, and intra-company STO exchanges stock within the same company code without billing.
What is the STO process in SAP MM?
The STO process in SAP MM entails generating an STO, shipping goods from the supplying plant, and stock-taking the received goods at the receiving plant.
What is the two-step STO process in SAP?
The two-step STO process issues goods at the supplying plant before and goods receipt at the receiving plant after, to track in-transit stocks.
What is the difference between STO and Purchase Order (PO) in SAP?
Internal transfers of stock among plants use an STO, whereas a Purchase Order (PO) is used to source materials from external suppliers.
